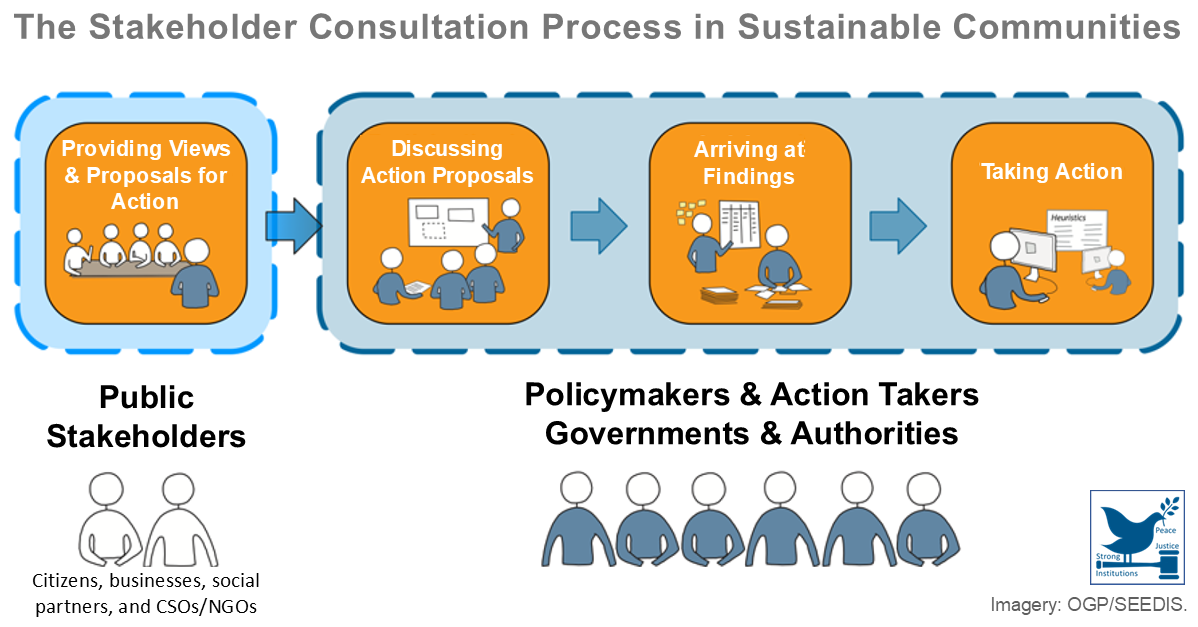
This report reveals that company executives are the most significant source of pressure behind corporate commitments to supply chain sustainability (SCS). Given their central role in setting and steering strategies, this suggests that the drive toward supply chain sustainability is a long-term business trend. The report sheds light on how companies put their SCS commitments into practice. Three common approaches emerged: supplier development, supply chain visibility, and environmental impact reduction. The trend is driven primarily by large and very large companies. Small- and medium-sized companies are less likely to engage until after the coronavirus crisis due to strained financial resources
This report reveals that company executives are the most significant source of pressure behind corporate commitments to supply chain sustainability (SCS). Given their central role in setting and steering strategies, this suggests that the drive toward supply chain sustainability is a long-term business trend. The report sheds light on how companies put their SCS commitments into practice. Three common approaches emerged: supplier development, supply chain visibility, and environmental impact reduction. The trend is driven primarily by large and very large companies. Small- and medium-sized companies are less likely to engage until after the coronavirus crisis due to strained financial resources
Bateman, Alexis, Kellen Betts, Ken Cottrill, Jason Pang, and Aniruddha Suhas Deshpande. "State of Supply Chain Sustainability 2021". MIT Center for Transportation & Logistics and Council of Supply Chain Management Professionals. (x1640908800)2021. https://sscs.mit.edu/...
Posted on 26/11/21
Recent Abstracts

The Anthropocene Reality of Financial Risk
Financial services are critical for corporate activities to regenerate and promote biosphere resilience as a key strategy to confront the new risk landscape and are essential to the transformation needed for a sustainable future. Current financial risk frameworks focus mainly on financial materiality and risks to the f ...
Posted on 16/06/24

Perceptions of Stakeholders on Nature-Based Solutions in Urban Planning: A Thematic Analysis in Six European Cities
Numerous social and ecological benefits are associated with nature-based solutions (NBS). This study gathered the views of stakeholders engaged in urban planning regarding the importance of nature-based solutions (NBS). The findings revealed that stakeholders perceive numerous social and ecological advantages associa ...
Posted on 13/06/24
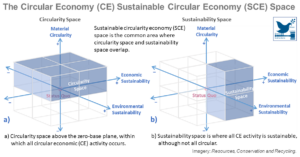
Why ‘Circular’ Doesn’t Always Mean ‘Sustainable’
Material circularity (MC) develops positively when a material is circulated through reuse, refurbishment, remanufacture, or recycling at its highest quality, it usually being measured through material flow analysis (MFA). When economic value is generated as commonly measured through life cycle costing (LCC), economic ...
Posted on 12/06/24

Build Resilient Infrastructure, Promote Inclusive and Sustainable Industrialization and Foster Innovation
SDG 9 of the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) sets out eight targets and twelve indicators used to monitor the achievement of the goals. With more than half of the world's population living in cities, mass transport, renewable energy and carbon reduction call for solutions and new industries and information and ...
Posted on 07/06/24
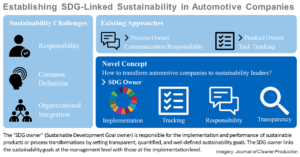
On Influencing Factors for Sustainable Development Goal Prioritisation in the Automotive Industry
Sustainability has become a key corporate strategy inspiring companies to implement the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). This paper identifies the SDG priorities in the automotive industry worldwide, from the point of view of the geographic, cultural, social, and economic specifics of the countries in which th ...
Posted on 06/06/24

Fifth National Climate Assessment: Understanding Risks, Impacts, and Responses
Adaptation planning more effectively reduces climate risk when it identifies not only disparities in how people are affected by climate change but also the underlying causes of climate vulnerability. Transformative adaptation involves consideration of the physical and social drivers of vulnerability and how they inter ...
Posted on 05/06/24

Net zero city: The Timeline of Increasing Urgency
During the past decade, more renewable power was added to the grid annually than fossil fuel and nuclear power combined. Renewable technologies dominate the global energy market for new electricity generation capacity simply because they have become the cheapest sources of electricity in many markets. 260 gigawatts of ...
Posted on 03/06/24

For critical minerals, it’s better to talk about SDGs than ESG
Economic strategies aim to drive research and innovation, develop bilateral and multilateral partnerships further economic reconciliation with indigenous peoples. Among the most recognizable values credentials companies use to demonstrate their commitment to best practices are environmental, social, and governance (ESG ...
Posted on 31/05/24

Nature Positive: Guidelines for the Transition in Cities
A crucial shift is required in urban development away from solely preventing climate change towards environmental action that protects and restores nature. Cities can advance their nature-positive transition and expedite restorative and renaturalization actions to benefit and reap the rewards of a sustainable and resi ...
Posted on 30/05/24
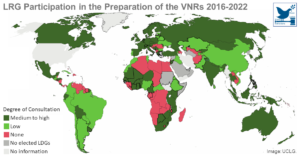
Towards the Localization of the SDGs
To accelerate SDG localization and sustainable local and regional development, national governments must urgently implement an enabling framework for subnational governments to meet their devolved responsibilities and the demands of the communities. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a holistic agenda intend ...
Posted on 29/05/24

Climate Change Denial
Climate change denial is a form of science denial characterized by rejecting, refusing to acknowledge, disputing or fighting the scientific consensus on climate change. It refers to denial, dismissal, or doubt of the scientific consensus on the rate and extent of global warming, its significance, or its connection to ...
Posted on 28/05/24
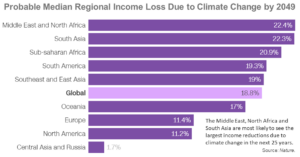
Ten Facts about the Economics of Climate Change and Climate Policy
The world’s climate has already changed measurably in response to accumulating greenhouse gas (GHG). Considerable uncertainties surround both the extent of future climate change and the biophysical impacts of such change. Despite the uncertainties, climate scientists strongly agree that in the absence of measures to si ...
Posted on 14/05/24

The differential impact of climate interventions along the political divide in 60 countries
A major barrier to climate change mitigation is the political polarization of climate change beliefs. In a global experiment, the differential impact of eleven climate interventions across the ideological divide were assessed. This paper examines the political polarization of climate change at the level of beliefs and ...
Posted on 13/05/24
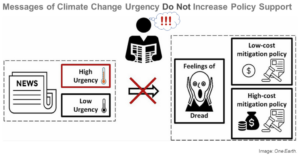
The IPCC Report and the Need for Radical Climate Action
The UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report demonstrates that climate breakdown is happening more quickly than anticipated and warns that much of the planet will soon become uninhabitable. The science-driven report emphasizes the urgent need for radical climate action to stay in a climate safety zon ...
Posted on 11/05/24
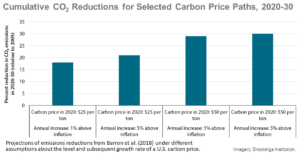
Navigating the Risks of Greenwashing in the Voluntary Carbon Market
Voluntary carbon markets (VCMs) offer an important market mechanism for firms to efficiently abate their emissions. By utilizing the VCM, they can buy verified carbon credits (VCCs) from carbon projects that have a lower marginal cost of abatement. One of the main obstacles in delivering the lowest cost abatement throu ...
Posted on 08/05/24