GRI. "Universal Standards". https://www.globalreporting.org/...
 The GRI Standards are global public reporting best practices on economic, environmental and social impacts. Reporting based on the standards provides information about an organization’s positive or negative contributions towards sustainable development for integration into its strategy, to identify financial risks and evaluate its long-term success. The standards contain disclosures and include requirements and recommendations. Requirements specify information an organization must report or instructions it must comply with and report. Recommendations suggest additional voluntary information or a course of action. They provide a structure for reporting relevant information about an organization and its economic, environmental and social impacts.
The GRI Standards are global public reporting best practices on economic, environmental and social impacts. Reporting based on the standards provides information about an organization’s positive or negative contributions towards sustainable development for integration into its strategy, to identify financial risks and evaluate its long-term success. The standards contain disclosures and include requirements and recommendations. Requirements specify information an organization must report or instructions it must comply with and report. Recommendations suggest additional voluntary information or a course of action. They provide a structure for reporting relevant information about an organization and its economic, environmental and social impacts.
Posted on 17/11/21
Recent Abstracts
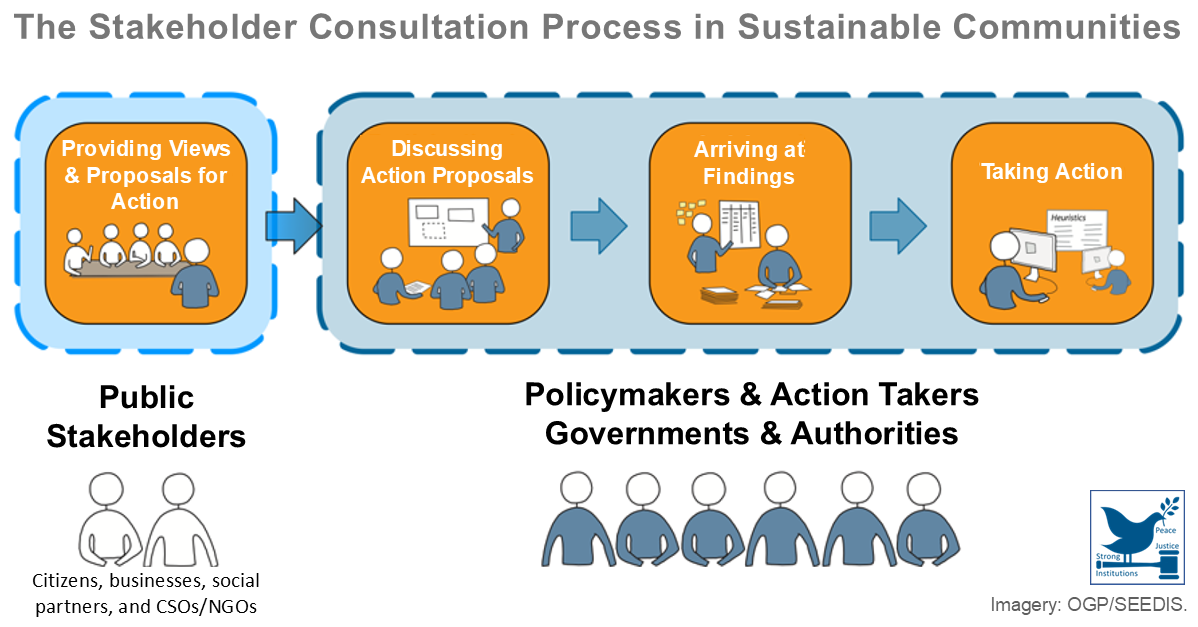
OECD Toolkit for a Territorial Approach to the SDGs
This action checklist helps government policymakers in uptaking, implementing, and localizing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), as a tool for better policies and living quality. It covers (1) policies and strategies, (2) multi-level governance, (3) financing and budgeting, (4) data and information, and (5) sta ...
Posted on 03/10/22
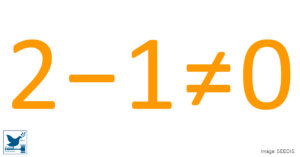
The Great Carbon Capture Scam
The oil industry invented “net zero” as the perfect alternative to slowing oil production to halt global heating. The netting deducts some carbon from total CO₂ emissions to create “net zero emissions”. The oil industry thereby claims to capture and store CO₂, while using this “captured carbon” for enhanced oil recov ...
Posted on 30/09/22
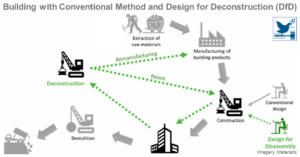
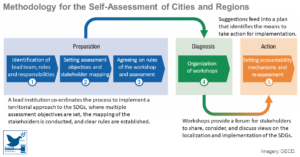
Key Approaches to Construction Circularity: A Systematic Review of the Current State and Future Opportunities
Construction circularity is identified in 1) material design, 2) building design, 3) construction and facility management, 4) urban sustainability development, and 5) system precondition. These five broad categories represent different levels of circularity implementation in construction and can be further decomposed ...
Posted on 28/09/22
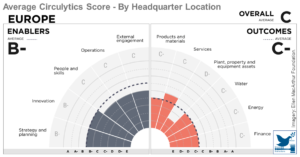
Material Circularity Indicator (MCI)
The Material Circularity Indicator (MCI) allows companies to identify circular value from their products and materials and mitigate risks from material price volatility and material supply. It enables users to analyze and evaluate a range of environmental, regulatory, and supply chain risks for their designs and produ ...
Posted on 26/09/22
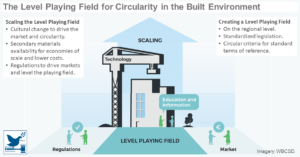
Scaling the Circular Built Environment: Pathways for Business and Government
The private and public sectors need to create a level playing field for circular materials, products and services to become the new normal in the built environment. The transition to a circular economy calls for introducing new valuation methods and implementing long-term policies that encourage the scaling of circula ...
Posted on 23/09/22

The Framing of a Sustainable Development Goals Assessment in Decarbonizing the Construction Industry – Avoiding “Greenwashing”
To avoid the use of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) for greenwashing, construction projects must include both long-term and short-term factors in assessing their SDG sustainability. However, companies rarely use SDG assessments as a tool for decisions for real change towards more sustainable and equitable cor ...
Posted on 21/09/22

Asset Management Industry Confronts the Challenges Presented by Climate Change Transition
Climate change transition and a rapidly evolving regulatory landscape confront the asset management industry with considerable challenges and present risks and opportunities for investing. Asset managers must strengthen disclosure of the climate-related risks and opportunities and support “sustainability” initiatives ...
Posted on 19/09/22

Talking a Good Game: Stop Paying Lip Service to Collaboration
Collaboration with businesses, public institutions, and civil society organizations is generally seen with a thumbs-up or a comment on a social media posting. Individuals often express interest in engaging in a collaborative initiative, but seldom follow through with collaborative action. This article suggests that w ...
Posted on 16/09/22
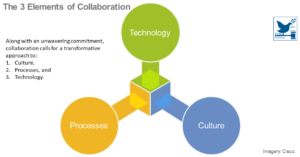
The Collaboration Imperative
The earth’s atmosphere, natural resources, and biological ecosystems are of fundamental value to business and society, much of which is destroyed through the ways we use these complex and fragile systems. Meeting the challenges of climate change, resource depletion, and ecosystem loss calls for improved collaboration ...
Posted on 14/09/22
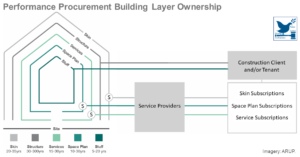
From Principles to Practices: Realising the Value of Circular Economy
This report demonstrates to real estate investors and construction clients the value and process of implementing circular economy principles in the built environment. How value is created from real estate assets is determined and established by investors and construction clients through investment requirements, tenure ...
Posted on 09/09/22
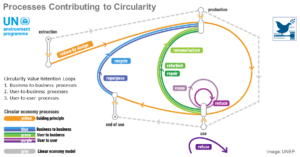
Applying Principles of Circular Economy to Sustainable Tourism
The circular tourism model must be implemented immediately for us not to exceed the ecological ceiling through the polluting practices of our current linear tourism model and to ensure tourism does not fall short on the social factors. As the tourism has a multiplier effect, it could be a catalyst to move the whole ec ...
Posted on 07/09/22
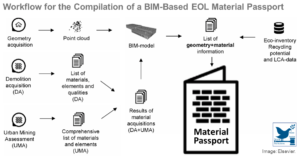
Material Passports for the End-of-Life Stage of Buildings: Challenges and Potentials
Global consumption of non-renewable resources is increasing and shortages of primary raw materials and reduction of space for final waste disposal are raising urgent issues for our communities. The unsustainable use of resources is resulting in strategies for maximizing recycling rates and minimizing environmental imp ...
Posted on 05/09/22
GrünStattGrau
The platform is an interface between network partners from the public sector, science and research, and community stakeholders that shares best practices in developing sustainable communities. It inspires and advances the deployment of technologies, competencies, and services and furthers the affordability of tools an ...
Posted on 02/09/22
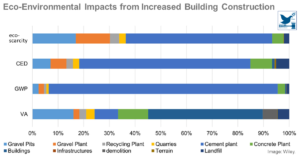
Regional Circular Economy of Building Materials: Environmental and Economic Assessment Combining Material Flow Analysis, Input-Output Analyses, and Life Cycle Assessment
Especially in terms of resource availability, spatial planning, or economic performance, the constraints for development policies in regions can differ widely. A model-based assessment on a regional scale enables policy decisions to consider sustainability and offers significant advantages over a mere product-level ap ...
Posted on 31/08/22
A Framework for Building Efficient Environmental Permitting Processes
Public participation can be an effective instrument in facilitating the building permitting process. A collaborative permitting process must enable stakeholders to voice concerns and openly discuss the permit. Although public participation generally lengthens the process, it provides opportunities for public comment ...
Posted on 26/08/22