CO₂ emissions from burning wood to generate heat can be 150% higher per unit of energy produced than from natural gas and 30% higher than from coal. Harvesting trees for heat releases carbon into the atmosphere that would otherwise have remained sequestered in the forest and forgoes increasing carbon capture as the trees continue to grow. It takes a long time for the increase in CO₂ emissions from burning wood for energy to be offset by the CO₂ absorbed by the regrowing tree. However, policymakers largely deny or ignore the harmful effects and facts of burning wood on climate change.
CO₂ emissions from burning wood to generate heat can be 150% higher per unit of energy produced than from natural gas and 30% higher than from coal. Harvesting trees for heat releases carbon into the atmosphere that would otherwise have remained sequestered in the forest and forgoes increasing carbon capture as the trees continue to grow. It takes a long time for the increase in CO₂ emissions from burning wood for energy to be offset by the CO₂ absorbed by the regrowing tree. However, policymakers largely deny or ignore the harmful effects and facts of burning wood on climate change.
Hanson, Craig, and Janet Ranganathan. "INSIDER: Why Burning Trees for Energy Harms the Climate". Insights. December 06, 2017. https://www.wri.org/...
Posted on 09/11/24
Recent Abstracts

Financing Circularity: Demystifying Finance for Circular Economies
Circular economy strategies can be achieved using such financial instruments as green bonds, green loans, sustainability-linked loans and circular leasing. Sustainability-linked finance calls for innovative business models and financing that integrates circularity in discrete development projects and for general corpo ...
Posted on 12/11/24
Circular City Actions Framework – Bringing the Circular Economy to Every City
A circular community promotes an equitable transition to sustainability across the urban space through multiple city functions and departments in cross-sectoral collaboration with research institutions, local businesses, and community residents. In a circular economy, existing materials that were once used in a produc ...
Posted on 11/11/24

How Does Nuclear Energy Affect the Environment?
Nuclear energy is propagated by science, companies, and governments as a source of clean energy source, as opposed to CO₂-producing plants. However, the effects nuclear energy has on the environment pose serious threats that cannot be ignored or greenwashed. The principal environmental and safety concerns are CO₂ emi ...
Posted on 08/11/24
SDGs: Top Trumps of Sustainable Finance?
Private finance is essential for meeting the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). To mobilize the finance and harness capital flows for sustainable development and investing, the investment community must make sense of the SDGs. For this, a global benchmarking tool, SDG rating harmonization, a globally adopted taxon ...
Posted on 05/11/24

What is Circular Economy and Why does It Matter?
Our current economic system can be considered a “linear economy”, built on a model of extracting raw materials from nature, turning them into products, and then discarding them as waste. Currently, only 7.2% of used materials are cycled back into our economies after use. This has a significant burden on the environme ...
Posted on 23/10/24

Fixing the Economy to Fix Climate Change
We need to change the way we think about climate change in order to reduce greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs) and meet the targets set out in the Paris Agreement. Energy efficiency and switching to renewable energy is only half the story. It is vital, but would only address 55% of global emissions. To reach net-zero, we a ...
Posted on 23/10/24
The Skill Requirements of the Circular Economy
In response to global challenges regarding resource scarcity and environmental concerns, the circular economy (CE) has emerged as a transformative model focused on resource efficiency and waste reduction. As the discourse intensifies, understanding the skill requirements of CE becomes imperative for effective policy-m ...
Posted on 23/10/24

Climate Science Denial
The fact of dangerous anthropogenic global warming (AGW) is now accepted by all but an insignificant number of climatologists worldwide, by every major national and international scientific society, and by every major nonpartisan humanitarian and economic organization. This chapter in the book The Truth About Denial: ...
Posted on 20/10/24
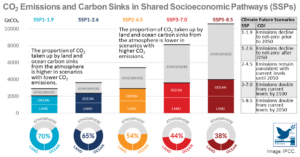
‘It’s Now or Never’: UN Climate Report’s 4 Urgent Takeaways
According to the recent IPCC report, "Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change", if urgent action is not taken immediately, humanity won't limit warming to 1.5°C – the threshold for more devastating fires, drought, storms, and other anthropogenic environmental disasters. At their presently rising levels, howe ...
Posted on 01/09/24
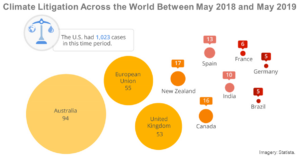
Turning Up the Heat: Corporate Legal Accountability for Climate Change
Strategic litigation encourages corporate accountability for climate change and broader corporate accountability movements when governments have repeatedly failed to take steps to adequately combat climate change. Climate lawsuits against companies are the result of increased collaboration between concerned individual ...
Posted on 30/08/24

Conceptualizing the Circular Economy (Revisited): An Analysis of 221 Definitions
Circular economy (CE) is based on reduction, reuse and recycling, regardless of whether it is conceptualized as a 3R framework covering the 3R dimensions of reduction, reuse, recycling, as a 4R framework that considers the 4R dimensions of reduction, reuse, recycling, recovery, or as an x-R framework that includes 4R. ...
Posted on 22/08/24

Scientists on Twitter: Preaching to the Choir or Singing from the Rooftops?
Socioeconomic decision-making and policy changes are affected and realized through public awareness. This calls for active engagement by the scientists and researchers with the public and the intended audience, which can drive or be driven by science and scientific research. Scientists must engage decision-makers and ...
Posted on 02/08/24
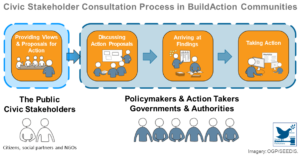
Deliberation – Getting Policy-Making Out From Behind Closed Doors
Governments commonly use deliberation as a part of the policy-making process, but it is usually conducted internally and behind closed doors, thereby excluding the public. However, efforts to involve the public in the deliberative stage are quite rare and, for the most part, governments do not have a reliable methodol ...
Posted on 26/07/24
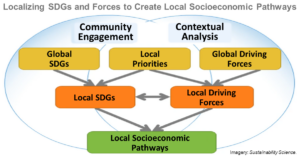
Co-Creating Local Socioeconomic Pathways for Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) recognize the importance of action locally for achieving socioeconomic sustainability globally. Local communities must focus on a locally relevant subset of goals and understand potential future pathways for key drivers that influence local sustainability to contribute to natio ...
Posted on 25/07/24
Adaptation of the Building Sector to Climate Change: 10 Principles for Effective Action
We are witnessing unprecedented climate change due to the rapidly increasing concentration of CO₂ in the atmosphere. Climate change is having severe consequences for communities that are designed for steady climatic conditions – not for the predicted climate extremes. Data collected over the recent decades shows that ...
Posted on 19/07/24