CO₂ emissions from burning wood to generate heat can be 150% higher per unit of energy produced than from natural gas and 30% higher than from coal. Harvesting trees for heat releases carbon into the atmosphere that would otherwise have remained sequestered in the forest and forgoes increasing carbon capture as the trees continue to grow. It takes a long time for the increase in CO₂ emissions from burning wood for energy to be offset by the CO₂ absorbed by the regrowing tree. However, policymakers largely deny or ignore the harmful effects and facts of burning wood on climate change.
CO₂ emissions from burning wood to generate heat can be 150% higher per unit of energy produced than from natural gas and 30% higher than from coal. Harvesting trees for heat releases carbon into the atmosphere that would otherwise have remained sequestered in the forest and forgoes increasing carbon capture as the trees continue to grow. It takes a long time for the increase in CO₂ emissions from burning wood for energy to be offset by the CO₂ absorbed by the regrowing tree. However, policymakers largely deny or ignore the harmful effects and facts of burning wood on climate change.
Hanson, Craig, and Janet Ranganathan. "INSIDER: Why Burning Trees for Energy Harms the Climate". Insights. December 06, 2017. https://www.wri.org/...
Posted on 09/11/24
Recent Abstracts
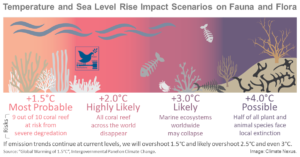
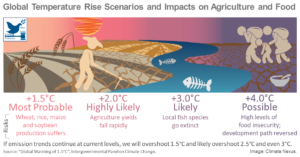
When Will Climate Change Make the Earth Too Hot For Humans?
This essay is the result of numerous interviews, decades of scientific research, and abstract mathematics of climate change about the possible end of the world as we know it. We’re told that it’s worse than we could possibly imagine and whatever we fear, we’re “barely scratching the surface of what terrors are possibl ...
Posted on 10/08/23

Environmental Law and the Unsustainability of Sustainable Development: A Tale of Disenchantment and of Hope
The sustainable development principle drives environmentally destructive neoliberal economic growth that exploits and degrades the local ecology. Despite well-meaning intentions behind sustainable development, it facilitates exploitative economic development activities that exacerbate systemic inequalities and injustic ...
Posted on 07/08/23
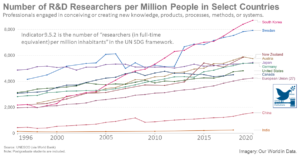
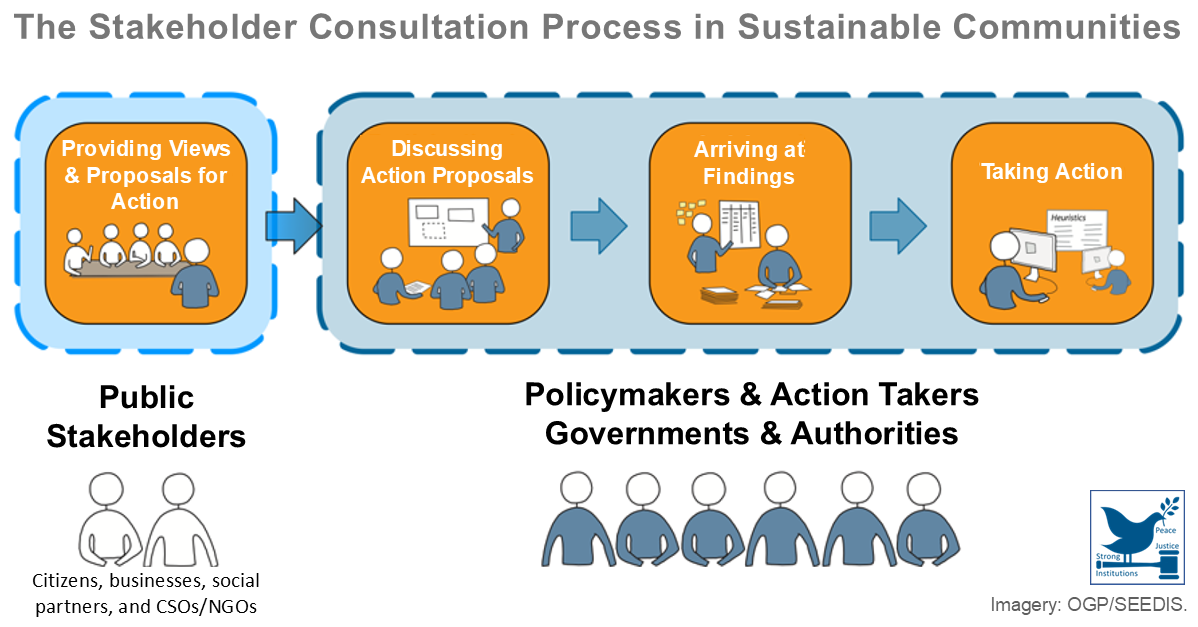
Sustainable Development Goal 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
Sustainable Development Goal 9 is to “build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation”, according to the United Nations. For SDG 9, the UN has defined 8 targets that specify the goals and 12 indicators that represent the metrics by which the world aims to track ...
Posted on 03/08/23
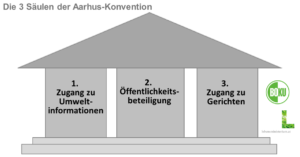
Rechtliche Optionen zur Verbesserung des Zugangs zu Gerichten im österreichischen Umweltrecht gemäß der Aarhus-Konvention (Artikel 9 Absatz 3)
„Der Natur und Umwelt eine Stimme geben!“ – So oder ähnlich könnte man das Anliegen der 1998 unter der Schirmherrschaft der UNECE geschlossenen Aarhus-Konvention umschreiben. Auch Österreich ist diesem internationalen Abkommen beigetreten, das es sich zum Ziel gesetzt hat, die Durchsetzung des Umweltrechts mit Hilfe d ...
Posted on 03/08/23
Access to Justice: Remedies – Article 9.4 of the Aarhus Convention and the Requirement for Adequate and Effective Remedies, Including Injunctive Relief
To hinder environmental damage and obtain a protective order or injunction in most civil law systems, danger in delay must be asserted for the enforceability of proceedings. To initiate legal proceedings, a 𝘱𝘳𝘪𝘮𝘢 𝘧𝘢𝘤𝘪𝘦 case must exist, requiring the claimant to present evidence and show the likelihood of success on the ...
Posted on 31/07/23
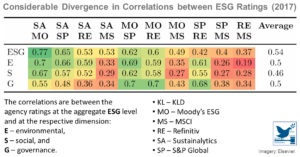
Aggregate Confusion: The Divergence of ESG Ratings
The divergence of ESG ratings creates uncertainty and represents a challenge for decision-makers, including investment managers and regulators. This ESG rating divergence makes it difficult to evaluate the ESG performance of companies, funds, and portfolios, which is their primary purpose. It also decreases companies’ ...
Posted on 25/07/23

Mars, Stephen Hawking and the Selfish Gene: Why Humans Are Programmed to Self-Destruct Wherever We Go
Speaking for humanity, Bezos claims that we don’t want to live in a “retrograde world” where we’d have to freeze population growth. Elon Musk says colonization on other planets is a necessity to ensure that the human race survives. Richard Branson is again exploiting astronomical business opportunities with commercia ...
Posted on 20/07/23

Why ESG is Failing Sustainable Development
Financial markets are the principal means for financing socioeconomic activity and achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Governments and financial market regulators define the parameters and incentives within which market participants make investment and financing decisions and operate, while the provide ...
Posted on 16/07/23

Sustainable Fitch: Climate Scenario Limitations Are Surfacing as Usage Rises
Climate scenario analysis is a key tool for evaluating complex physical and transition risks of companies and communities. This raises questions about the credibility of transition plans and long-term risk management processes that do not apply the scenarios. Limited standardization and transparency make it difficult ...
Posted on 02/07/23
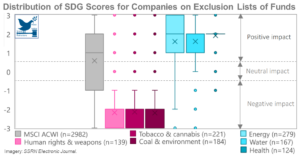
ESG to SDG: Do Sustainable Investing Ratings Align with the Sustainability Preferences of Investors, Regulators, and Scientists?
While ESG and SDG are complementary, they cannot be used interchangeably to identify the sustainability of companies and their contribution to social development and the planet. Where sustainable investors aim to invest in companies that contribute to sustainable development, there is disagreement on how best to measu ...
Posted on 27/06/23
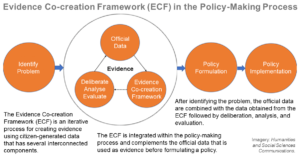
Translating Citizen-Generated Air Quality Data into Evidence for Shaping Policy
The practice of participatory sensing for environment monitoring has rapidly evolved over the years. There has been a steady growth of citizen-based environmental monitoring projects that aim to build partnerships, knowledge-sharing platforms, awareness, and ultimately environmental resilience. Citizen science has resh ...
Posted on 04/06/23

Assessing ‘Good Governance’ and Corruption in New Zealand: ‘Scientific’ Measurement, Political Discourse, and Historical Narrative
New Zealand is ranked highly on the Worldwide Governance Indicators (WGI), which assess performance on six dimensions of governance: voice and accountability, political stability and absence of violence, government effectiveness, regulatory quality, rule of law, and control of corruption. Moreover, New Zealand has long ...
Posted on 02/04/23
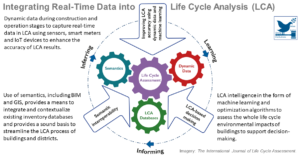
The Application of Life Cycle Assessment in Buildings: Challenges, and Directions for Future Research
New generation life cycle assessment (LCA) methods and tools can positively influence the environmental impact of the built environment and help mitigate the effects of climate change. They continuously learn from real-time data while allowing for effective operation and management strategies of buildings and district ...
Posted on 28/10/22
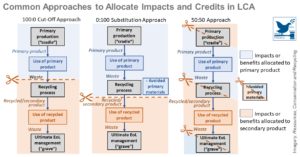
Towards Sustainable Development through the Circular Economy—A Review and Critical Assessment on Current Circularity Metrics
The circular economy (CE) is an optimal pathway to sustainable development and companies, governments and academics have formulated various proposals to measure circularity. Ideally, circularity metrics indicate how well circularity is applied to the whole life cycle of products and services in terms of society, the e ...
Posted on 24/10/22

What are the challenges in assessing circular economy for the built environment? A literature review on integrating LCA, LCC and S-LCA in life cycle sustainability assessment, LCSA
For circular economy (CE) to succeed, focus must be given to the service life phase and the reuse/recycle phase of building projects. This involves more stakeholders both in the early decision-making phases of projects as well as in the design phase and impacts the project value chain. Life cycle sustainability asses ...
Posted on 19/10/22