Climate change denial is a form of science denial characterized by rejecting, refusing to acknowledge, disputing or fighting the scientific consensus on climate change. It refers to denial, dismissal, or doubt of the scientific consensus on the rate and extent of global warming, its significance, or its connection to human behavior, in whole or in part and is a form of science denial that can take pseudo-scientific forms. Climate change denial includes unreasonable doubts about the extent to which climate change is caused by humans, its effects on nature and human society, and the potential of adaptation to global warming by human actions. Climate change denial can also be implicit when people accept the science but fail to reconcile it with their belief or actions.
Climate change denial is a form of science denial characterized by rejecting, refusing to acknowledge, disputing or fighting the scientific consensus on climate change. It refers to denial, dismissal, or doubt of the scientific consensus on the rate and extent of global warming, its significance, or its connection to human behavior, in whole or in part and is a form of science denial that can take pseudo-scientific forms. Climate change denial includes unreasonable doubts about the extent to which climate change is caused by humans, its effects on nature and human society, and the potential of adaptation to global warming by human actions. Climate change denial can also be implicit when people accept the science but fail to reconcile it with their belief or actions.
Wikipedia. "Climate Change Denial". Accessed May 27, 2024. https://en.wikipedia.org/...
Posted on 28/05/24
Recent Abstracts

2024 SDG Report: Global Progress Alarmingly Insufficient
The 2024 Sustainable Development Goals Report highlighted that nearly half the 17 targets are showing minimal or moderate progress, while over a one-third are stalled or going in reverse, since they were adopted by UN Member States back in 2015 to bring peace and prosperity for people and the planet. “This report is k ...
Posted on 18/03/25

U.S. Rejects UN Sustainable Development Goals
The U.S. under the Trump administration stated that it “rejects and denounces” the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs), the key global goals adopted by nations unanimously in 2015 as part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, aimed at tackling global environmental and social challenges. Th ...
Posted on 18/03/25

The Role of Green Buildings in Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals
Numerous environmental, social, and economic development challenges are covered under the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and green building plays a key role of in achieving the UN’s SDGs. Overcoming barriers and the adoption of solutions and methods to integrate non-renewable and renewable resources is a promisi ...
Posted on 14/03/25

Trump 2.0: An Assault on Science Anywhere is an Assault on Science Everywhere
The Trump administration has launched an unfounded assault on science and initiatives, on research institutions and international organizations and on academic freedom and people’s rights. It is firing employees from national agencies in key disciplines that protect public health, the environment and people’s safety a ...
Posted on 13/03/25

Trump Trade War vs Sustainability
A trade war occurs when countries impose tariffs or other barriers on each other’s goods, which can lead to a global conflict that unsettles global trade relations. When major players like the United States, the European Union, and China engage in trade disputes, entire sectors that depend on global collaboration and ...
Posted on 12/03/25
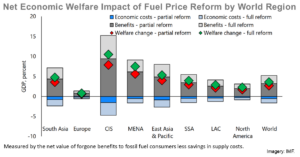
IMF Fossil Fuel Subsidies Data: 2023 Update
Globally, fossil fuel subsidies were $7 trillion in 2022 or 7.1% of GDP. Explicit subsidies – the undercharging for supply costs – have more than doubled since 2020. This equals 18% of the total subsidy, while nearly 60% is due to undercharging for global warming and local air pollution. Differences between efficien ...
Posted on 11/03/25

The United Nations Sustainable Development Cooperation Framework (UNSDCF)
The United Nations Sustainable Development Cooperation Framework (UNSDCF) is the most important instrument for planning and implementation of the UN development activities at country level. The Cooperation Framework is an agreement between the UN and the host government that must a) clearly articulate the United Natio ...
Posted on 10/03/25
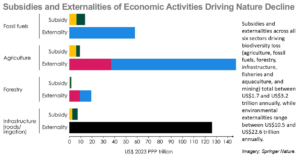
The Costs of Subsidies and Externalities of Economic Activities Driving Nature Decline
A better understanding of the complexity, size, design, and effects of subsidies and externalities of economic sectors contributing to environmental degradation could facilitate and expedite discussions to strengthen the implementation of multilateral agreements. This is an essential aspect of the global economic syst ...
Posted on 10/03/25

Global Trade is Fracturing: Here’s Why the EU Needs the Green Deal More Than Ever
President Trump is weaponizing trade. After decades of globalization and expanding trade, recent shocks have exposed the fragility of global value chains (GVCs). As rising geopolitical tensions fuel protectionist sentiments and trade wars, the urgent need for sustainable and environmentally friendly supply chains fo ...
Posted on 21/02/25

A Transformation Strategy with Manifold Socio Economic Benefits for India and Germany
Current patterns of production and consumption, in particular in the global North, cannot be transferred to the rising world population, in particular in the global South, without severe environmental and societal consequences and economic risks. The “Green Economy” is intended to “contribute to eradicating poverty as ...
Posted on 17/02/25

On the Role of Construction in Achieving the SDGs
Construction and real estate have been central to the debates on sustainable development. Where the dominant definition of sustainability in the built environment focuses on the environmental dimension, the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) offer opportunities for the building sector to expand its focus. Green ...
Posted on 05/02/25
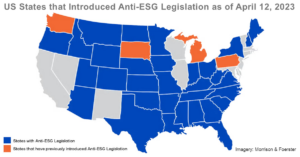
Gas, Guns, and Governments: Financial Costs of Anti-ESG Policies
Restricting ESG strategies distorts financial market outcomes. As investor interest in funds with environmental, social and governance (ESG) principles has increased, legislation restricting public sector activity with funds that pursue ESG-friendly principles has been proposed or passed in 17 states. As a result, th ...
Posted on 03/02/25

Allianz Risk Barometer – Identifying the Major Business Risks for 2025
Over the last two decades, the global re/insurance sector has experienced an increasing number of major natural catastrophes, such as winter storms, forest fires, severe heat waves and heavy flooding. Countries around the world are suffering the effects of climate change, which contribute to more frequent and extreme ...
Posted on 31/01/25

Correlates of Climate Change Skepticism
Climate change is a highly contentious topic that has led to such labels such as “alarmists” and “deniers”. While the former urge immediate and drastic action to stop global climate change, the latter deny many of the key claims made by scientists about climate change. Among other, less extreme groups, are the “skept ...
Posted on 29/01/25
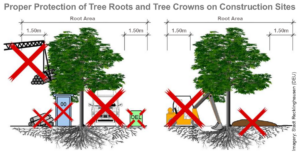
Vienna Tree Protection Act in Austria
The Vienna Tree Protection Act is considered one of the factors that makes Vienna the “most liveable city” in the world. While Vienna has a highly effective and strictly enforced tree protection ordinance, the rest of Austria vehemently resists such strict nature conservation measures. Regulations to protect trees an ...
Posted on 28/01/25