Wikipedia. "Climate Change Denial". Accessed May 27, 2024. https://en.wikipedia.org/...
 Climate change denial is a form of science denial characterized by rejecting, refusing to acknowledge, disputing or fighting the scientific consensus on climate change. It refers to denial, dismissal, or doubt of the scientific consensus on the rate and extent of global warming, its significance, or its connection to human behavior, in whole or in part and is a form of science denial that can take pseudo-scientific forms. Climate change denial includes unreasonable doubts about the extent to which climate change is caused by humans, its effects on nature and human society, and the potential of adaptation to global warming by human actions. Climate change denial can also be implicit when people accept the science but fail to reconcile it with their belief or actions.
Climate change denial is a form of science denial characterized by rejecting, refusing to acknowledge, disputing or fighting the scientific consensus on climate change. It refers to denial, dismissal, or doubt of the scientific consensus on the rate and extent of global warming, its significance, or its connection to human behavior, in whole or in part and is a form of science denial that can take pseudo-scientific forms. Climate change denial includes unreasonable doubts about the extent to which climate change is caused by humans, its effects on nature and human society, and the potential of adaptation to global warming by human actions. Climate change denial can also be implicit when people accept the science but fail to reconcile it with their belief or actions.
Posted on 28/05/24
Recent Abstracts

What’s Lost When We Talk ‘ESG’ and Not ‘Sustainability’
Corporate profitability is the sole purpose of ESG (environment, social and governance) disclosure, not sustainable development per se. SDG achievement for the sustainability of the biosphere and socio-economic environment of the world for all stakeholders is not the intended purpose of ESG. Instead, it focuses on pr ...
Posted on 30/05/22

Environmental Sustainability Strategies for Smaller Companies in the Hotel Industry: Doing the Right Thing or Doing Things Right?
For most hotels, environmental issues are not a response to societal challenges – doing the right thing – but rather a response to owners’ concerns – doing things right. Tourism is a predator of natural resources and tourism practices do not correspond to essential consuming acts. This paper explores the strategic re ...
Posted on 27/05/22

Hotel Sustainability Certifications
For hotels, environmental certification depends on their life cycle stage when analyzed. Different versions of environmental certifications are available for new builds and existing structures as well as the assessment of the sustainability of the operation of the buildings and business. Hotels, which generally requi ...
Posted on 25/05/22
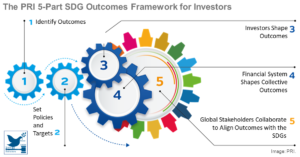
Comparative Study of Key Supply Chain Management Elements in Sustainability Reports
For the evaluation of enterprise value and investment decision-making, firms must demonstrate their commitment to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). For this, several factors are considered, including supply chain management (SCM), human rights, climate change, safety, and environmental risks. This study analy ...
Posted on 23/05/22

Nexus Between Life Cycle Assessment, Circularity, and Sustainability Indicators – Part I: A Review
Sustainable building design influences life cycle costs (LCC) and the level of circularity (LoC) and calls for use of life cycle assessment (LCA) and circularity indicator-based approaches. Depending on the product and the circular economy (CE) scenarios, different types of connections – beneficial, conditional, or sc ...
Posted on 16/05/22

A Parametric Approach to Optimizing Building Construction Systems and Carbon Footprint: A Case Study Inspired by Circularity Principles
The principles of circularity for the sustainable design of buildings aim to reduce their environmental impact. Environmental product declarations (EPD) and carbon footprint tools are the most useful tools for classifying building materials and evaluating circular projects. Other life cycle assessment (LCA) tools are ...
Posted on 13/05/22
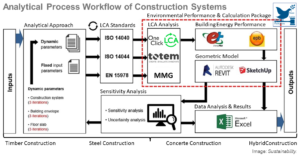
The New Net Zero
Owners, designers, contractors, and manufacturers must radically rethink the way we use, renovate, and design buildings. Using better and less materials is key to reducing embodied carbon in meeting our CO₂ emission targets. For this, tracking the environmental impacts of the whole building life cycle – from material ...
Posted on 11/05/22
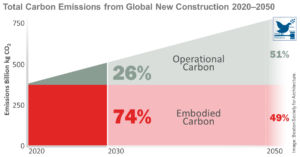
AIA-CLF Embodied Carbon Toolkit
To decarbonize buildings, architects and building designers must reduce the environmental footprint and CO2 emissions associated with materials over the whole life cycle of building. Through life cycle assessment (LCA), the highest-impact, most cost-effective solutions to reducing embodied carbon are identified. This ...
Posted on 09/05/22
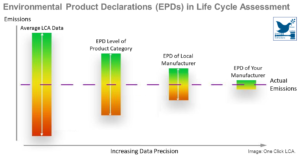
Sustainable Material Selection – A Guide
Construction is responsible for a huge amount of emissions and environmental degradation. How and by whom materials are made is key to transitioning to a sustainable economy. An important tool in assessing the ecological impacts is environmental product declarations (EPD), which are product-specific impact assessment ...
Posted on 06/05/22
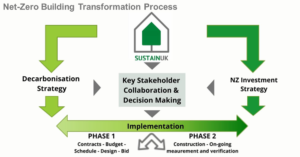
Net-Zero Building Optimisation
SustainUK is inviting you to UK Construction Week London 2022, delivering the largest built environment exhibition at ExCeL London on 3-5 May 2022. SustainUK facilitates and mainstreams Paris-aligned sustainable building development and to overcome real or perceived barriers. SustainUK's collaborative sustainability pr ...
Posted on 03/05/22
Climate Claims against Governments in Europe
Environmental claims are part of the movement in seeking justice and taking legal action to promote social, economic and environmental sustainability. State and EU-level climate action and policies are being challenged for being insufficient to limit the global average temperature increase to below 2°C, as stipulated i ...
Posted on 02/05/22

GlobalABC Roadmap for Buildings and Construction: Towards a Zero-Emission, Efficient and Resilient Buildings and Construction Sector
Decarbonizing buildings across their entire life cycle calls for the transformation of the buildings and construction sector. The transformation requires greater collaboration among policymakers at all jurisdictional levels as well as with urban planners, architects, developers, investors, construction companies, and ...
Posted on 29/04/22

EU Green Deal Product Regulations – What It Means for Design and Construction
The Sustainable Products Initiative (SPI) is a regulatory framework comprising a set of legislative files that aims to boost the circularity of the EU’s single market. The European Commission (EC) proposed the regulation on March 30 2022 intending to make sustainable products the norm in the EU, facilitate circular bu ...
Posted on 27/04/22
City Policy Framework for Dramatically Reducing Embodied Carbon
This is a framework for cities and other government bodies to develop a strategy, action plan, and policies in response to the climate emergency. It is a manual and blueprint to dramatically reduce embodied carbon from the manufacture, transport, use, and life-cycle end of construction material. It helps cities in re ...
Posted on 25/04/22

Taking Governments to Court: Climate Litigation and Its Consequences
Climate legal action is increasingly being taken against national governments. Litigation has successfully forced some countries to radically improve on their commitments to tackle the effects and limit the extent of anthropogenic climate change. This paper examines three recent European cases that produced landmark ...
Posted on 23/04/22